Application lifetime
Birth of application
Applications are born in the MyApp/config.jsxinc file in form of the configuration object that is passed to the application manager. It si method BX.apps.add(config)API, where BX.apps is instance of the AppManagerAPI class, config is an object according to the ApplicationAPI specification and may additionally contain autorun, application and id property.
Script may contain more applications.
Doing jobs
Application receives tasks in the form of requests. Request is usually a string that is sent via BX.apps.processRequest(id, request)API method to the application with this id.
If application configuration contains the autorun property, application manager immediately initializes this application and sends autorun request.
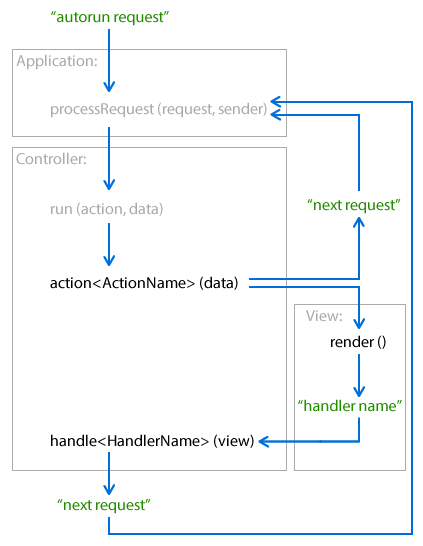
Processing of the request
Application: processRequest(request, sender)API
Brixy framework calls this method for you. You do not care about it.
- It translates the request to the route. Route object wraps the controller and its action method, optionally some data.
- Invokes the
run(action, data)API method of the controller. - If controller returns a new request, application processes it.
Controller: run(action, data)API
Brixy framework calls this method for you. You do not care about it.
action<ActionName>(data)method of the controller is called here. Controller's subclass should define required action methods, e.g.actionDefault(data)for'Default'action.- Calls
View.render(data)API method if controller's action method initializes some view viasetView(view, data)API method. - Calls
handle<HandlerName>(view)method if yourView.render(data)method returns a handler name. run()method may return the next application request. Application will process it.
Controller: action<ActionName>(data)
You should make this method for each your controller.
- Controller does the action task in this method. E.g. communicates with the model layer of the application to get and/or set some data.
- If some user inputs are required, you can call
setView(view, data)API method to initialize your View class. - The action method may return the application request. Controller's
run()method will return it to the application.
View: render(data)API
Brixy framework calls this method for you. You do not care about it. Simply define your view class with render() method.
- Shows dialog window to get some data from the user.
- Method may return the name of the controller's handler. Controller's subclass should define required handler methods, e.g.
handleSave(view)for'Save'handler.
Controller: handle<HandlerName>(view)
You should make this method if you want handle data from the user input.
- This method finishes the task of the current action after the end of the view rendering. The view with user data is accessible as argument of this method.
- The handle method may return the application request. Controller's
run()method will return it to the application.
Processing of application events
Application events are intended for inter-application communication. Script can even publish a method for calling application events from the outside world, e.g. from CEP application.
Events are called via BX.apps.processEvent(event, data)API method. Application manager sends the event to all applications that listens this event.
The end of the application
Standard script ends when the last application request is finished.
Script running in the persistent Extend Script engine remains alive for the duration of the Adobe application. Application can process requests and events all this time.
Edited: 2017/09/14